
Knee pain occurs among patients of all ages and lifestyles. This pain is seen during physical activity for a variety of reasons: from an injury or bruise to significant illness and inflammation. Ignoring it can have serious consequences. A common question is what to do if you have pain? At the first painful sensation, it is recommended to consult a doctor to avoid hospitalization, treatment should be carried out only by a doctor.
The first manifestation of knee pain is usually caused by heavy loads, wear and deformation of the joints. The disease is felt not only during excessive stress, but also at rest, during rest and during everyday activities. In this article we will see why the knee hurts, the main methods of diagnosis and treatment.
What is the knee joint?
The knee joint of our body carries a large load and body weight, accounting for most injuries and stress during falls, sports and lifting heavy objects. The knee joint itself is one of the largest joints in our body.
The knee joint includes:
- the joint itself;
- muscles;
- ball joint;
- menisci;
- joint capsule;
- ends of the femur and tibia,
- ships,
- nerves,
- ligaments
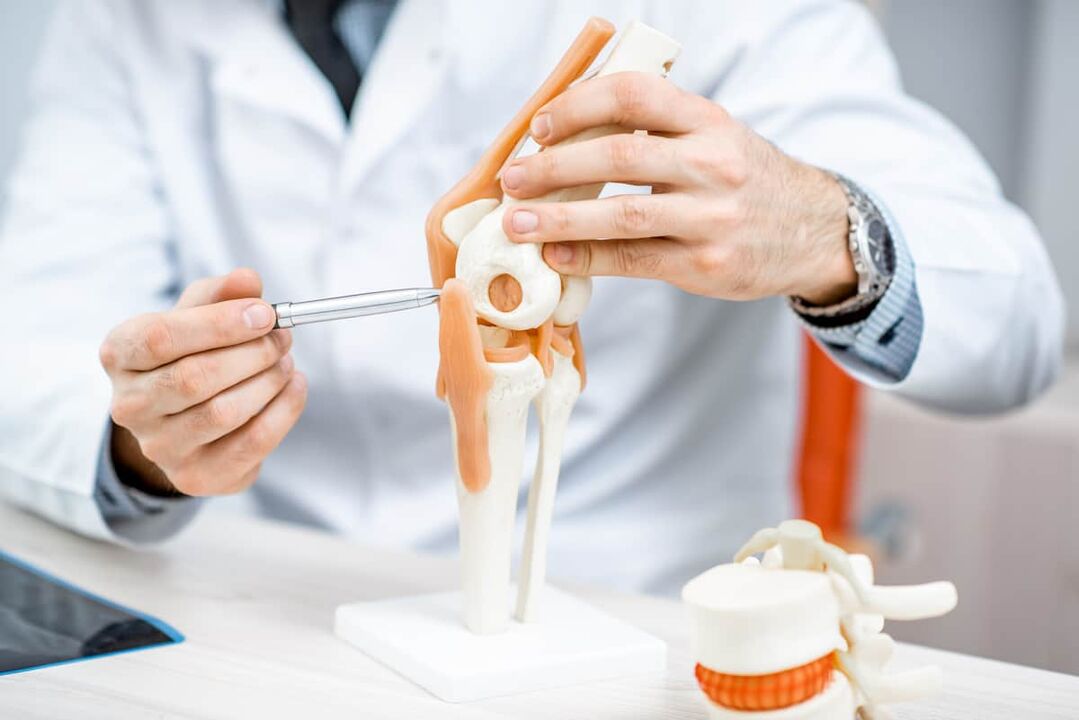
Each of these components is susceptible to damage, although pain is not always felt immediately. For example, with a dislocated or torn meniscus and a torn ACL, mobility will be reduced and vascular damage will lead to a hematoma. Infection can begin in the knee joint capsule after infectious diseases. If the patient has a neurological disease, stabbing pain may be felt in the knee. In addition, it can radiate to the joint with pain in the femur, tibia and muscles.
Causes of joint pain
The nature of pain can be divided into two groups: acute and chronic. Acute pain is characterized by progressive and rapidly developing pathologies. Chronic diseases, on the other hand, are quite slow and require lifelong treatment. The causes of this pain vary and so does the treatment.
Let's look at the main causes of pain.
Pain due to injuries.
The cause of acute pain is injuries and various traumatic actions. You can get injured from a bad fall, from playing sports, or from uncomfortable shoes. The pain begins to be felt a few days after the injury. Generally the knee has slight swelling and victims experience quite tolerable pain. Depending on the severity of the injury, abrasions may appear on the surface of the skin. In addition, excess weight, the abuse of bad habits and the peculiarities of the profession and work increase the risk of injury.
Types of injury:
- Bruise on the knee.Frequent and minor damage. Swelling and redness appear in the knee area, and the surface temperature increases. Even a minor injury to the knee can lead to the destruction of joint tissue cells.
- Sprains.Sometimes a muscle, ligament or tendon sprain goes unnoticed and causes sharp, stabbing pain in the knee, and the joint itself becomes unstable when stepping on the leg.
- Ligament rupture.It can appear due to strong twisting of the leg in an unnatural direction and causes severe pain, swelling and swelling.
- Meniscus tear.It appears as a result of a heavy load, a blow to the knee, a twist of the leg and due to its unnatural position. A torn meniscus causes the legs to stop moving normally. It often occurs in athletes and is accompanied by swelling, bleeding, and inability to bend the leg. There is a rule regarding sports: the knee may hurt, but it should go away the next morning after training. If the disease does not go away, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
- Joint fracture.Due to the fracture, the soft tissues are also damaged, causing severe pain and deformation of the knee.
Unpleasant sensations in the knee are not always characterized by a disease in this section. Sometimes a herniated disc can cause knee pain at night. Discomfort can also occur if the knee joint is used too little and the associated muscles lose tone.
Asymmetry of the sacrum and pelvic bones can also cause pain in the knee joint. It occurs as a result of a difference in the length of the lower extremities, which can be a consequence of congenital characteristics or curvature of the pelvis, even due to scoliosis.
Knee diseases
Any inflammation or damage to the structure of the knee causes discomfort, especially when moving. And the infection is not always located in the knee itself. In general joint diseases, the entire body is affected and the knees are damaged the most due to intense stress. Additionally, in case of injuries or diseases of the spine, or fracture of the femoral neck, pain in the knee joint may appear. Let's look at some of them:
- ArthritisIt is an inflammatory process that develops after trauma from an infection or metabolic problems. If left untreated, the cartilage in the knee joints continues to progressively wear away, causing increased pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis– an autoimmune disease in which the body's defense cells negatively affect the tissue. The joint loses mobility, swelling appears, pain is constantly present and manifests itself in an increased feeling of stiffness.
- Rheumatism– as a rule, adolescents are susceptible to it, as well as people who have recently suffered from streptococcal diseases. Characterized by alternating unpleasant sensations.
- Gonarthrosis (osteoarthritis).It develops in one or both knees. This disease is characterized by the appearance of degenerative-dystrophic processes with growth of connective and bone tissue that interferes with movement. At the beginning of the disease, discomfort begins to be felt only after a long walk, but as the disease progresses, pain begins to appear even after walking short distances. It is difficult to get up from a chair, squat, or climb stairs. Pain doesn't just bother you at rest. Destruction or thinning of the cartilage tissue that absorbs impacts occurs. As gonarthrosis develops, a crunch in the knee and deformation of the joint are noted.
- Reactive arthritis– begins a few days after an intestinal infection. Severe pain combined with swelling and redness of the skin over the right or left knee usually indicates reactive arthritis.
- Bursitis– inflammation of the joint capsule, which causes severe pain and discomfort during movement.
- periarthritis– inflammation of the tendons, muscles and ligaments surrounding the knee joint. Painful sensations appear with increased load on the bent leg.
- Chondropathy– destruction of the cartilage that surrounds the knee joint and cushions friction and shock.
- Neoplasms– When they appear, the vessels are compressed and the joint capsule is deformed, causing pain and limiting mobility.
- Osteoporosis– the tissues weaken, become more brittle, the calcium content in the bones gradually decreases.
- Osteomyelitis– Inflammation of the bone tissue appears in the affected area, accompanied by swelling, fever and intense acute pain.
- Osteoarthritis– Inflammation of the joint capsule gradually localizes to the heads of the bones. The cartilage wears down and thins, causing the bone heads to no longer slide easily when moving the limb. Aching pain occurs.
- Osteoarthritis– a disease that affects all components of the joint.
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome– often occurs in young patients. During physical activity, the kneecap moves forward. This happens due to incorrect position of the foot, excessive and heavy loads with unprepared muscles.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease– knee pain when bending, climbing stairs, squatting.
- Nerve damage and disorders of nervous tissue.Sharp pains, numbness and tingling appear in the lower limb and loss of mobility. A pinched nerve appears due to inflammation, neoplasms or previous injuries. Or neuritis develops - inflammation of the nerve in one or more areas. Severe pain is felt, mobility and sensitivity are reduced, and the limb contracts involuntarily.
- Impaired blood supply.
- Various other infectious diseases.The complications that arise contribute to the appearance of weakness and pain.
In addition to the listed diseases, others can contribute to the appearance of pain: synovitis, ligamentitis, tendinitis, gout, neuropathy, cysts and others.
Thus, pain in the knee is always a sign of a pathological process that affects the cartilaginous, bone or soft tissue structures of the knee itself, or of damage to the nerve that innervates it.
Diagnosis of knee pain.
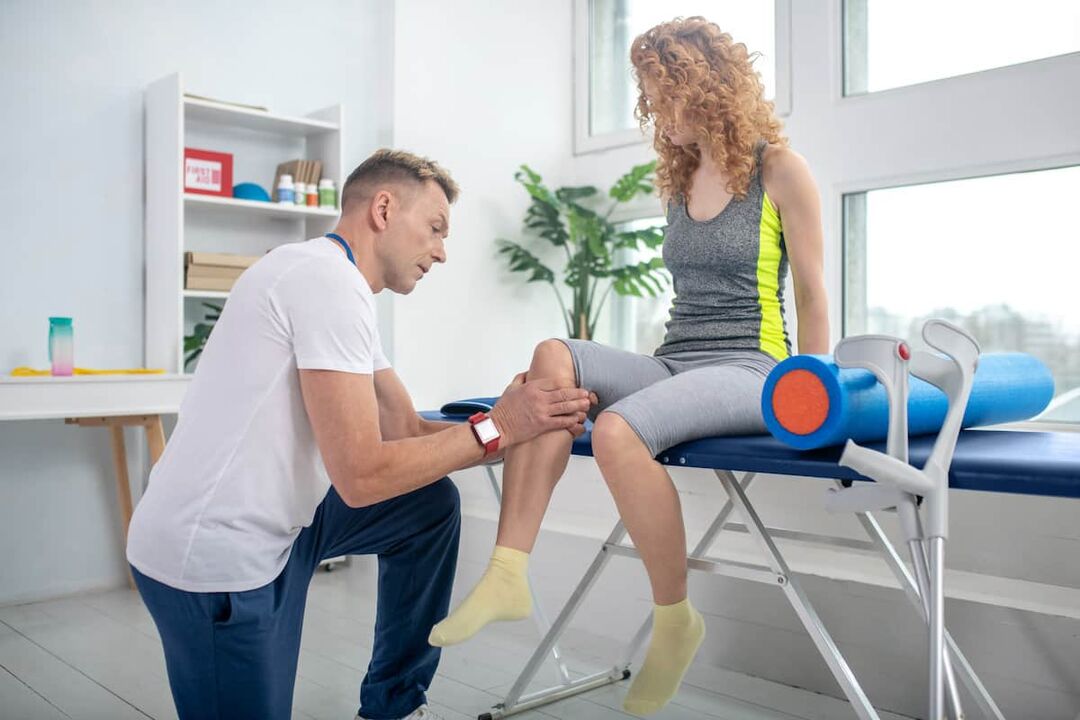

To start treatment, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis by a doctor in the clinic using diagnostic measures.
The patient makes an appointment with an osteopath, orthopedic traumatologist, surgeon or rheumatologist. If necessary, after examination and examination, the patient can be sent to another specialist.
At the appointment, the doctor collects a history: complaints, symptoms and problems that concern the patient, infections and chronic diseases. After this, the doctor may palpate the area of interest and ask the patient to perform various movements and tests. For example, bend and straighten your knee. This will provide initial information about the degree of discomfort.
To obtain additional information and determine an accurate diagnosis, the patient is sent for one or more examinations:
- radiography (X-ray);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) therapy;
- computed tomography (CT);
- arthroscopy (a special instrument, an endoscope, is inserted into the joint);
- puncture to collect synovial fluid;
- laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests, serological tests).
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are used to diagnose nervous diseases, depending on contraindications. Some diagnoses require more precise tests.
To relieve knee pain, you can see an osteopath, physical therapist, chiropractor, or massage therapist. An osteopath will help restore the normal position of the pelvic bones and internal organs, which has a positive effect on their functioning, improve the nutrition of all spinal structures by activating blood circulation, and improve posture by eliminating deformities of the spine. column.
Knee pain treatment
It is impossible to choose the best knee pain medication yourself. This is due to the fact that it is first necessary to find out the true cause of the symptoms and determine the type of pathological disorders in the body.
Treatment of the knee joint is carried out comprehensively. This set of measures includes:
- medicinal (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories or chondroprotectors; their effectiveness lies in preserving moisture in the cartilage cells, inhibiting enzymatic action and stopping the degenerative process);
- preparations, solutions for external use;
- osteopathy;
- performing special exercises and gymnastics, physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy techniques;
- massages;
- Vitamin complexes are drugs indicated to improve the body's metabolic processes.
Various types of physical therapy treatments can be used to treat musculoskeletal disorders that cause knee pain.
Physiotherapy classes are simple and accessible to people of any age, as an individually designed program ensures the creation of a precisely dosed load. For complex therapies, local analgesics are also prescribed, for example, ointment with dimethyl sulfoxide (there are contraindications: serious diseases of the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular system, pregnancy, lactation) or an anti-inflammatory gel - it is instantly absorbed into the skin. , penetrates into its deep layers, relieves swelling and pain.
Pain can also be eliminated using high-frequency techniques: morphological changes remain, but the pain decreases and becomes milder. In addition, special orthoses are often prescribed: bandages, knee pads, splints, tapes, casts and other similar devices. This allows you to transfer the load from the knee and unload it, reducing the risk of reinjury and promoting rapid rehabilitation. Plasmolifting is rarely used: injections of plasma obtained from the patient's own blood directly into the affected knee joint or into the soft tissue surrounding it.
Sometimes a bone realignment procedure or surgery is performed (for example, if bone fragments need to be removed).
The doctor also prescribes pain relievers that do not have any negative effect on the articular cartilage.
Pay attention to your diet: a balanced diet can prevent inflammation.
If you have problems with your knee, you should not self-medicate and attend various procedures to avoid surgical intervention (operation) and possible complications. This attitude can only worsen the situation and a more serious and complex therapy will be necessary. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor who will establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe competent treatments, procedures and medications that will have an effect. Take care of yourself and your health!























